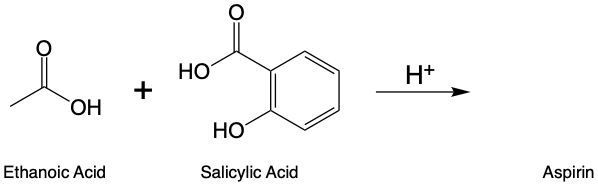
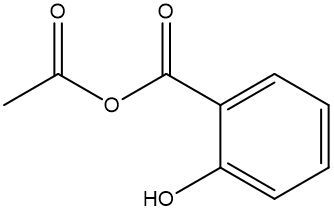
In this video, we're going to talk about esterification. Under this type of reaction, a carboxylic acid and an alcohol undergo a condensation reaction to form an ester. When we say condensation reaction, this is just a reaction that combines two molecules through the loss of water. Here, the carboxylic acid loses its OH portion, and the alcohol's oxygen loses its H portion. For this to happen, an H+ catalyst is required for the reaction to start.
So, if we take a look here at this basic depiction of esterification, we have a carboxylic acid. Remember, the squiggly line just means that it's connected to something else which we don't really care about. Over here, we have an alcohol, that's also connected to something else we don't care about. Focus on the OH of the carboxylic acid and the H of the alcohol oxygen. When they come into close contact with each other, we lose water. Remember, it's this H+ catalyst that gets the whole process going. Losing water, now this carbon needs to replace the bond that it just lost to the OH, and this oxygen needs to replace the bond that it just lost from losing its H. What do they do? They bond to each other. Here, we create an ester linkage. Remember, an ester group is when you have a carbonyl group connected to an oxygen, connected to a carbon. So, we just went from combining a carboxylic acid and an alcohol into an ester group. This is esterification through a condensation process.