Back
BackProblem 1
What results from the experiments of Frederick Griffith provided the strongest support for his conclusion that a transformation factor is responsible for heredity?
Problem 2
Explain why Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty's in vitro transformation experiment showed that DNA, but not RNA or protein, is the hereditary molecule.
Problem 3
Hershey and Chase selected the bacteriophage T2 for their experiment assessing the role of DNA in heredity because T2 contains protein and DNA, but not RNA. Explain why T2 was a good choice for this experiment.
Problem 4
Explain how the Hershey and Chase experiment identified DNA as the hereditary molecule.
Problem 5a
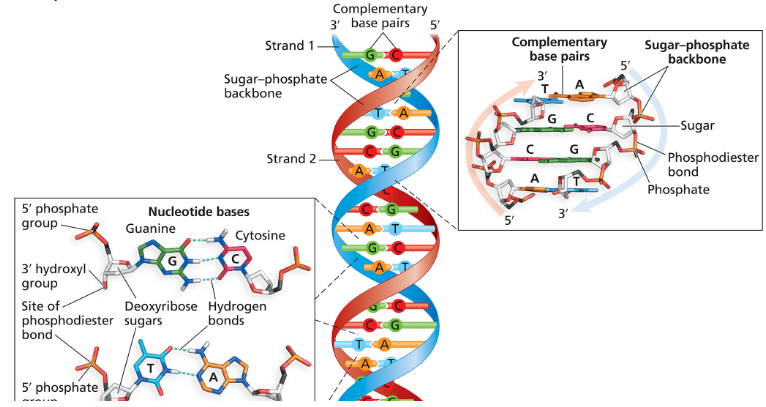
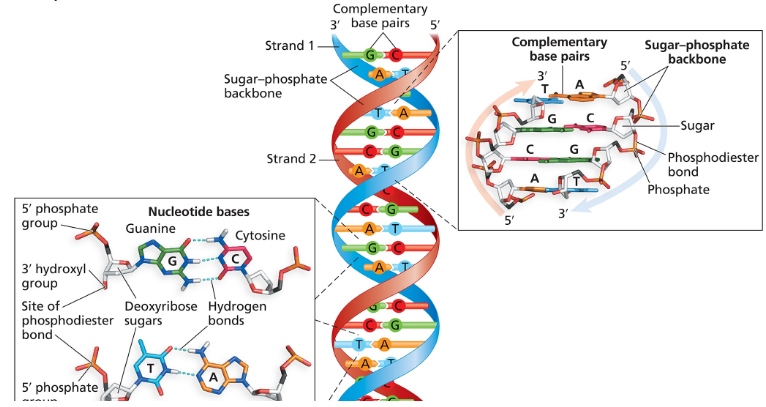
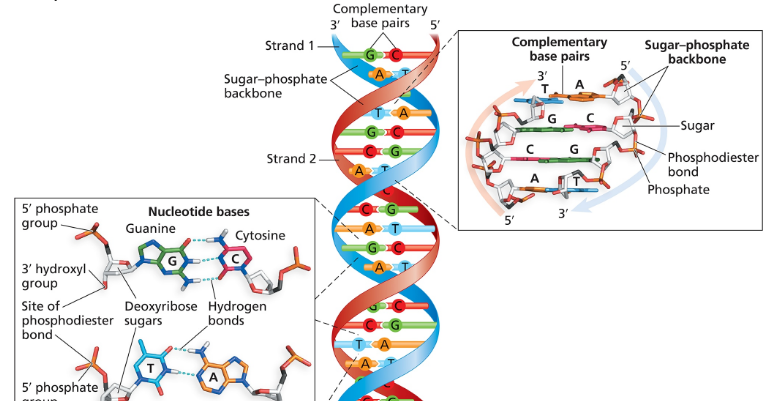
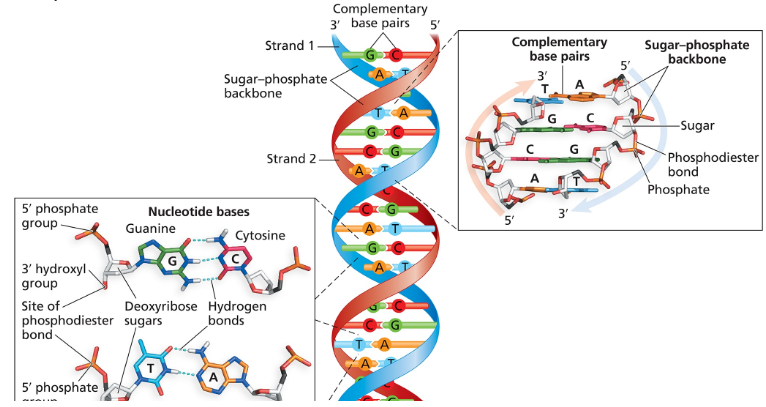
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What is the sequence of the other strand in the duplex?
Problem 5b
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What is the name of the bond that joins one nucleotide to another in the DNA strand?
Problem 5c
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
Is the bond in part (b) a covalent or a noncovalent bond?
Problem 5d
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
Which chemical groups of nucleotides react to form the bond in part (b)?
Problem 5e
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What enzymes catalyze the reaction in part (d)?
Problem 5f
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
Identify the bond that joins one strand of a DNA duplex to the other strand.
Problem 5g
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
Is the bond in part (f) a covalent or a noncovalent bond?
Problem 5h
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What term is used to describe the pattern of base pairing between one DNA strand and its partner in a duplex?
Problem 5i
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What term is used to describe the polarity of two DNA strands in a duplex?
Problem 6
The principles of complementary base pairing and antiparallel polarity of nucleic acid strands in a duplex are universal for the formation of nucleic acid duplexes. What is the chemical basis for this universality?
Problem 7
For the following fragment of DNA, determine the number of hydrogen bonds and the number of phosphodiester bonds present:
5'-ACGTAGAGTGCTC-3'
3'-TGCATCTCACGAG-5'
Problem 8a
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
What kind of bond joins the C to G within a single strand?
Problem 8b
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
What kind of bonds join the C in one strand to the G in the complementary strand?
Problem 8c
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
How many phosphodiester bonds are present in this DNA duplex?
Problem 8d
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
How many hydrogen bonds are present in this DNA duplex?
Problem 9a
Consider the sequence 3'-ACGCTACGTC-5'.
What is the double-stranded sequence?
Problem 9b
Consider the sequence 3'-ACGCTACGTC-5'.
What is the total number of covalent bonds joining the nucleotides in each strand?
Problem 9c
Consider the sequence 3'-ACGCTACGTC-5'.
What is the total number of noncovalent bonds joining the nucleotides of the complementary strands?
Problem 10
DNA polymerase III is the main DNA-synthesizing enzyme in bacteria. Describe how it carries out its role of elongating a strand of DNA.
Problem 11a
There is a problem completing the replication of linear chromosomes at their ends. Describe the problem and identify why telomeres shorten in each replication cycle.
Problem 11b
There is a problem completing the replication of linear chromosomes at their ends. What is the function of telomerase, and how does it operate to synthesize telomeres?
Problem 12
Explain how RNA participates in DNA replication.
Problem 13
A sample of double-stranded DNA is found to contain 20% cytosine. Determine the percentage of the three other DNA nucleotides in the sample.
Problem 14a
Bacterial DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III perform different functions during DNA replication.
Identify the principal functions of each molecule.
Problem 14b
Bacterial DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III perform different functions during DNA replication.
If mutation inactivated DNA polymerase I in a strain of E. coli, would the cell be able to replicate its DNA? If so, what kind of abnormalities would you expect to find in the cell?
Problem 14c
Bacterial DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III perform different functions during DNA replication.
If a strain of E. coli acquired a mutation that inactivated DNA polymerase III function, would the cell be able to replicate its DNA? Why or why not?