In Drosophila, the map positions of genes are given in map units numbering from one end of a chromosome to the other. The X chromosome of Drosophila is 66 m.u. long. The X-linked gene for body color—with two alleles, y⁺ for gray body and y for yellow body—resides at one end of the chromosome at map position 0.0. A nearby locus for eye color, with alleles w⁺ for red eye and w for white eye, is located at map position 1.5. A third X-linked gene, controlling bristle form, with f⁺ for normal bristles and f for forked bristles, is located at map position 56.7. At each locus the wild-type allele is dominant over the mutant allele.
Do you expect any of these gene pair(s) to assort independently? Explain your reasoning.
Calculate the mean, variance, and standard deviation for a sample of turkeys weighed at 8 weeks of age that have the following weights in ounces: 161, 172, 155, 173, 149, 177, 156, 174, 158, 162, 171, 181.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Mean
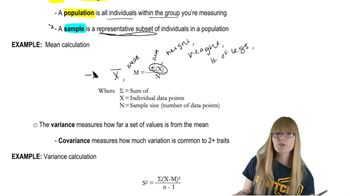
Variance

Standard Deviation

In Drosophila, the map positions of genes are given in map units numbering from one end of a chromosome to the other. The X chromosome of Drosophila is 66 m.u. long. The X-linked gene for body color—with two alleles, y⁺ for gray body and y for yellow body—resides at one end of the chromosome at map position 0.0. A nearby locus for eye color, with alleles w⁺ for red eye and w for white eye, is located at map position 1.5. A third X-linked gene, controlling bristle form, with f⁺ for normal bristles and f for forked bristles, is located at map position 56.7. At each locus the wild-type allele is dominant over the mutant allele.
A wild-type female fruit fly with the genotype y⁺w⁺f/ywf⁺ is crossed to a male fruit fly that has yellow body, white eye, and forked bristles. Predict the frequency of each progeny phenotype class produced by this mating.
In Drosophila, the map positions of genes are given in map units numbering from one end of a chromosome to the other. The X chromosome of Drosophila is 66 m.u. long. The X-linked gene for body color—with two alleles, y⁺ for gray body and y for yellow body—resides at one end of the chromosome at map position 0.0. A nearby locus for eye color, with alleles w⁺ for red eye and w for white eye, is located at map position 1.5. A third X-linked gene, controlling bristle form, with f⁺ for normal bristles and f for forked bristles, is located at map position 56.7. At each locus the wild-type allele is dominant over the mutant allele.
Explain how each of the predicted progeny classes is produced.
The ABO and MN blood groups are shown for four sets of parents (1 to 4) and four children (a to d). Recall that the ABO blood group has three alleles: I^A, I^B and i. The MN blood group has two codominant alleles, M and N. Using your knowledge of these genetic systems, match each child with every set of parents who might have conceived the child, and exclude any parental set that could not have conceived the child. <>
The wild-type color of horned beetles is black, although other colors are known. A black horned beetle from a pure-breeding strain is crossed to a pure-breeding green female beetle. All of their F₁ progeny are black. These F₁ are allowed to mate at random with one another, and 320 F₂ beetles are produced. The F₂ consists of 179 black, 81 green, and 60 brown. Use these data to explain the genetics of horned beetle color.
Provide a definition and an example for each of the following terms:
additive genes
