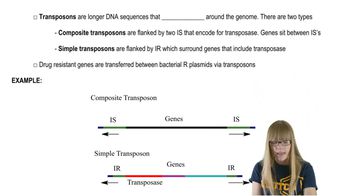
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Transposons
DNA transposons, also known as 'jumping genes,' are segments of DNA that can move from one location to another within the genome. They typically replicate through a 'cut and paste' mechanism, where the transposon is excised from its original position and inserted into a new site. This mobility can lead to genetic diversity and can influence gene expression and genome structure.
Recommended video:
Retrotransposons
Retrotransposons are a type of transposable element that replicate through an RNA intermediate. They are transcribed into RNA, which is then reverse-transcribed back into DNA and integrated into a new location in the genome. This process often involves the enzyme reverse transcriptase and can contribute to genomic evolution and variation.
Recommended video:
Eukaryotic Transposable Elements
Shared Properties of Transposons
Both DNA transposons and retrotransposons are mobile genetic elements that can change their position within the genome, contributing to genetic variability. They can both influence gene expression and play roles in evolution and adaptation. Additionally, both types can lead to mutations and genomic rearrangements, impacting the organism's phenotype.
Recommended video:
Prokaryotic Transposable Elements
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance