Classify each species as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base. d. CN–
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base from among the reactants in each equation. b. AlBr3 + NH3 ⇌ H3NAlBr3 c. F–(aq) + BF3(aq) ⇌ BF4–(aq)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Lewis Acids and Bases

Electron Pair Donation

Coordination Complex Formation
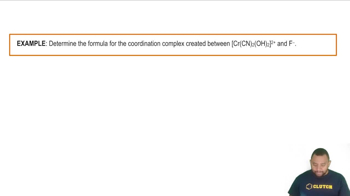
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base from among the reactants in each equation. a. Fe3+(aq) + 6 H2O(l) ⇌ Fe(H2O)63+(aq) b. Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) ⇌ Zn(NH3)42+(aq) c. (CH3)3N(g) + BF3(g) ⇌ (CH3)3NBF3(s)
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base from among the reactants in each equation. a. Ag+(aq) + 2 NH3(aq) ⇌ Ag(NH3)2+(aq)
Based on these molecular views, determine whether each pictured acid is weak or strong.
Based on these molecular views, determine whether each pictured acid is weak or strong.
The binding of oxygen by hemoglobin in the blood involves the equilibrium reaction: HbH+(aq) + O2(aq) ⇌ HbO2(aq) + H+(aq) In this equation, Hb is hemoglobin. The pH of normal human blood is highly controlled within a range of 7.35 to 7.45. Given the above equilibrium, why is this important? What would happen to the oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin if blood became too acidic (a dangerous condition known as acidosis)?
