Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis acids are substances that can accept an electron pair, while Lewis bases are those that can donate an electron pair. This definition expands the traditional Brønsted-Lowry concept of acids and bases, allowing for a broader range of chemical reactions to be analyzed. In the given reaction, identifying which species donates and which accepts electron pairs is crucial for determining the Lewis acid and base.
Recommended video:
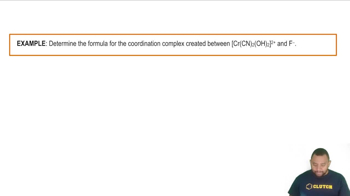
Coordination Complexes
Coordination complexes are formed when a central metal atom or ion binds to surrounding molecules or ions, known as ligands. In the provided equation, Fe3+ acts as the central metal ion, and H2O molecules serve as ligands. Understanding how these complexes form helps in identifying the roles of different species in the reaction.
Recommended video:
Coordination Complexes Example
Electron Pair Donation
Electron pair donation is a key process in Lewis acid-base chemistry, where a Lewis base donates a pair of electrons to a Lewis acid. This interaction leads to the formation of a new bond, resulting in a more stable complex. Recognizing which reactant donates the electron pair is essential for correctly identifying the Lewis base in the reaction.
Recommended video:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance