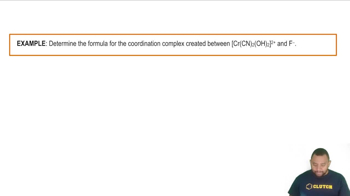
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis acids are species that can accept an electron pair, while Lewis bases are species that can donate an electron pair. This definition expands the concept of acids and bases beyond protons (H+) to include a broader range of chemical interactions, focusing on electron pair transfer.
Recommended video:
Electron Pair Donation
In the context of Lewis theory, electron pair donation is the process by which a Lewis base provides a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond with a Lewis acid. This interaction is fundamental in many chemical reactions, influencing the stability and reactivity of the resulting compounds.
Recommended video:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Charge and Coordination
The charge of a species plays a crucial role in determining its behavior as a Lewis acid or base. For example, positively charged species like Fe³⁺ are typically Lewis acids due to their ability to accept electron pairs, while negatively charged species like F⁻ can act as Lewis bases by donating electron pairs.
Recommended video:
Coordination Complexes Example
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance