Textbook Question
Draw the structures of two compounds that have the composition CH3NO2 and have all three H atoms bonded to the C. Predict which compound has the larger ONO bond angle.
623
views
 Tro 6th Edition
Tro 6th Edition Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory Problem 104
Problem 104 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

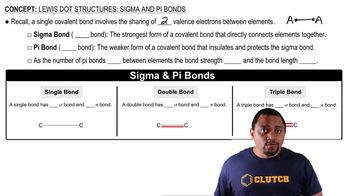

Draw the structures of two compounds that have the composition CH3NO2 and have all three H atoms bonded to the C. Predict which compound has the larger ONO bond angle.
How many types of hybrid orbitals do we use to describe each molecule? a. N2O5 c. BrCN (no formal charges)
How many types of hybrid orbitals do we use to describe each molecule? b. C2H5NO (four C-H bonds and one O-H bond)