Combustion analysis of naphthalene, a hydrocarbon used in mothballs, produces 8.80 g CO2 and 1.44 g H2O. Calculate the empirical formula of naphthalene.
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. H2C=CH−CH3 b. H3C−CH2−CH3 c. HC≡C−CH3 d. H3C−CH2−CH2−CH3

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Hydrocarbons

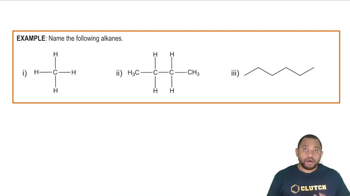
Alkanes
Alkenes and Alkynes

The foul odor of rancid butter is due largely to butyric acid, a compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Combustion analysis of a 4.30-g sample of butyric acid produces 8.59 g CO2 and 3.52 g H2O. Determine the empirical formula of butyric acid.
Tartaric acid is the white, powdery substance that coats tart candies such as Sour Patch Kids. Combustion analysis of a 12.01-g sample of tartaric acid—which contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen—produces 14.08 g CO2 and 4.32 g H2O. Determine the empirical formula of tartaric acid.
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. HC≡CH
How many molecules of ethanol (C2H5OH) (the alcohol in alcoholic beverages) are present in 145 mL of ethanol? The density of ethanol is 0.789 g/cm3.
A drop of water has a volume of approximately 0.05 mL. How many water molecules does it contain? The density of water is 1.0 g/cm3.
