Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Functional Groups
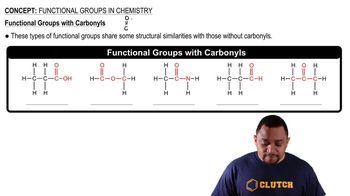
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In organic chemistry, the presence of a functional group, such as the hydroxyl group (-OH) in alcohols, determines the properties and reactivity of the compound. Recognizing functional groups is essential for naming organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method for naming organic chemical compounds. It provides rules for naming based on the structure of the molecule, including the longest carbon chain, the presence of functional groups, and the position of substituents. Understanding these rules is crucial for accurately naming compounds and communicating their structure.
Recommended video:
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations. In organic chemistry, isomers can exhibit different physical and chemical properties. Recognizing isomers is important for understanding the diversity of organic compounds and their potential reactivity.
Recommended video:
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance