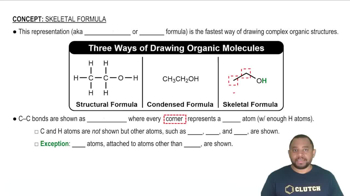
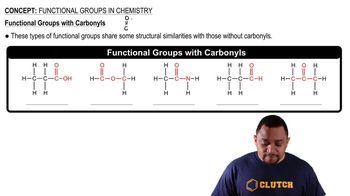
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nomenclature
Nomenclature in chemistry refers to the systematic naming of chemical compounds based on established rules. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides guidelines for naming organic and inorganic compounds, ensuring that each name conveys specific information about the compound's structure and composition.
Recommended video:
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula represents the elements in a compound and their respective quantities. It provides a concise way to convey the composition of a substance, such as H2O for water, indicating two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Understanding how to interpret and write chemical formulas is essential for naming compounds accurately.
Recommended video:
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. Recognizing functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH) or carboxyl (-COOH), is crucial for naming organic compounds, as they often dictate the compound's properties and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance