Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Charge and Electron Configuration
Ionic charge refers to the net electrical charge of an ion, which is determined by the loss or gain of electrons relative to the neutral atom. For example, a cation like Sr²⁺ has lost two electrons, while an anion like Br⁻ has gained one. Understanding how to calculate the number of electrons in an ion based on its charge is essential for completing the table.
Recommended video:
Electron Configuration Example
Atomic Number and Protons
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus and defines the element itself. For instance, chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17, meaning it has 17 protons. This number remains constant regardless of the ion's charge, which is crucial for determining the number of protons in the ions listed in the table.
Recommended video:
Relationship Between Electrons and Protons in Ions
In ions, the relationship between electrons and protons determines the overall charge. A neutral atom has equal numbers of protons and electrons, but in ions, this balance is disrupted. For example, in a Br⁻ ion, there are more electrons than protons, while in Sr²⁺, there are fewer electrons. This concept is vital for accurately filling in the blanks regarding the number of electrons in each ion.
Recommended video:
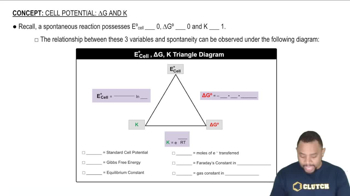
Relationship between ∆E°, ∆G°, and K
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance