Predict the charge of the ion formed by each element. a. Mg b. N d. Na
Ch.2 - Atoms & Elements
Chapter 2, Problem 65
Determine whether or not each element is a main-group element. a. tellurium b. potassium c. vanadium d. manganese
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the position of manganese on the periodic table. Manganese is represented by the symbol Mn and has an atomic number of 25.
Understand the structure of the periodic table, specifically the division between main-group elements and transition metals. Main-group elements are found in the s-block and p-block, while transition metals are located in the d-block.
Locate which block manganese falls into. Since manganese has an atomic number of 25, it is located in the d-block of the periodic table.
Recognize that elements in the d-block are classified as transition metals, not main-group elements.
Conclude that manganese, being a d-block element, is not a main-group element but rather a transition metal.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Main-Group Elements
Main-group elements, also known as representative elements, are found in groups 1, 2, and 13-18 of the periodic table. These elements typically exhibit a wide range of chemical properties and include metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. They are characterized by their valence electron configurations, which play a crucial role in determining their chemical behavior.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Main Group Elements: Density Example
Periodic Table Groups
The periodic table is organized into vertical columns called groups, which categorize elements based on similar properties and electron configurations. Elements in the same group often exhibit similar reactivity and bonding characteristics. Understanding the group placement of an element helps predict its chemical behavior and interactions with other elements.
Recommended video:
Guided course
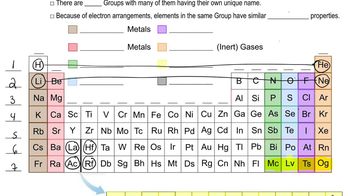
Periodic Table: Group Names
Transition Metals
Transition metals are found in groups 3 to 12 of the periodic table and are characterized by their ability to form variable oxidation states and complex ions. Manganese, specifically, is classified as a transition metal due to its position in group 7. This classification is important for understanding its chemical properties and its role in various chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Transition Metals
Related Practice
Textbook Question
731
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the blanks to complete the table.
Symbol Ion Formed Number of Electrons in Ion Number of Protons in Ion
Cl ______ ______ 17
Te ______ 54 ______
Br Br– ______ ______
______ Sr2+ ______ 38
1178
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Write the symbol for each element and classify it as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. a. gold b. fluorine c. sodium d. tin e. argon
1067
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not each element is a transition element. a. Cr b. Br c. Mo d. Cs
490
views
Textbook Question
Classify each element as an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, halogen, or noble gas. a. F b. Sr c. K d. Ne e. At
1508
views
Textbook Question
Which pair of elements do you expect to be most similar? Why? a. nitrogen and oxygen b. titanium and gallium c. lithium and sodium d. germanium and arsenic e. argon and bromine
1297
views
