Calculate the percent ionization of a formic acid solution having the given concentration. b. 0.500 M
Ch.17 - Acids and Bases
Chapter 17, Problem 75
A 0.148 M solution of a monoprotic acid has a percent ionization of 1.55%. Determine the acid ionization constant (Ka) for the acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given information: the concentration of the acid \([HA]\) is 0.148 M, and the percent ionization is 1.55%.
Calculate the concentration of ionized acid \([H^+]\) using the percent ionization: \([H^+] = \frac{\text{percent ionization}}{100} \times [HA]\).
Since the acid is monoprotic, the concentration of \([A^-]\) is equal to \([H^+]\).
Write the expression for the acid ionization constant \(K_a\): \(K_a = \frac{[H^+][A^-]}{[HA] - [H^+]}\).
Substitute the values of \([H^+]\), \([A^-]\), and \([HA]\) into the \(K_a\) expression and simplify to find \(K_a\).

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Monoprotic Acid
A monoprotic acid is an acid that can donate only one proton (H+) per molecule during the ionization process. This characteristic simplifies the calculation of its ionization constant, as the equilibrium expression involves only one dissociation step. Common examples include acetic acid and hydrochloric acid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Binary Acids
Percent Ionization
Percent ionization is a measure of the extent to which an acid dissociates in solution, expressed as a percentage of the initial concentration that has ionized. It is calculated using the formula: (concentration of ionized acid / initial concentration) × 100%. This concept helps in understanding the strength of the acid and its behavior in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
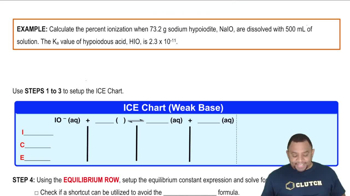
Percent Ionization Example
Acid Ionization Constant (Ka)
The acid ionization constant (Ka) quantifies the strength of an acid in solution, representing the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid into its ions. It is calculated using the formula: Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA], where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions, [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base, and [HA] is the concentration of the undissociated acid. A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Characteristics of Ka and Kb
Related Practice
Textbook Question
889
views
Textbook Question
Calculate the percent ionization of a formic acid solution having the given concentration. c. 0.100 M
343
views
Textbook Question
Calculate the percent ionization of a formic acid solution having the given concentration. d. 0.0500 M
419
views
Textbook Question
Find the pH of each mixture of acids. a. 0.115 M in HBr and 0.125 M in HCHO2
1892
views
Open Question
Find the pH of each mixture of acids. b. 0.150 M in HNO2 and 0.085 M in HNO3 c. 0.185 M in HCHO2 and 0.225 M in HC2H3O2 d. 0.050 M in acetic acid and 0.050 M in hydrocyanic acid
Open Question
Find the pH of each mixture of acids. a. 0.075 M in HNO3 and 0.175 M in HC7H5O2 b. 0.020 M in HBr and 0.015 M in HClO4 c. 0.095 M in HF and 0.225 M in HC6H5O d. 0.100 M in formic acid and 0.050 M in hypochlorous acid
