Open Question
Complete and balance each gas-evolution equation. b. HCl(aq) + KHCO3(aq) → c. HC2H3O2(aq) + NaHSO3(aq) → d. (NH4)2SO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) →
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


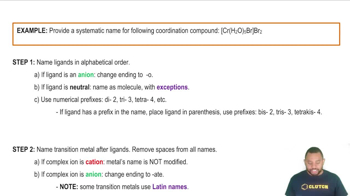
Complete and balance each gas-evolution equation. b. HCl(aq) + KHCO3(aq) → c. HC2H3O2(aq) + NaHSO3(aq) → d. (NH4)2SO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) →
Assign oxidation states to each atom in each element, ion, or compound. Ag, Ca2+, BaO, H2S, NO3-, CrO42-
Assign oxidation states to each atom in each element, ion, or compound. Cl2, Fe3+, CuCl2, CH4, Cr2O72–, HSO4–
What is the oxidation state of Cr in each compound? b. CrO3
What is the oxidation state of Cr in each compound? c. Cr2O3
What is the oxidation state of Cl in each ion? a. ClO- b. ClO2- c. ClO3- d. ClO4-