Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals bond together by sharing electrons. They are characterized by specific formulas that indicate the number of each type of atom present in the molecule. Understanding how to name and write formulas for these compounds is essential, as it reflects the composition and structure of the substance.
Recommended video:
Naming Molecular Compounds
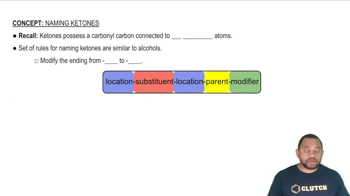
Naming Conventions
The naming of molecular compounds follows specific conventions, often using prefixes to denote the number of atoms of each element. For example, 'mono-' indicates one, 'di-' indicates two, and 'tri-' indicates three. This systematic approach helps in accurately conveying the composition of the compound, such as in 'dichlorine monoxide' for Cl2O.
Recommended video:
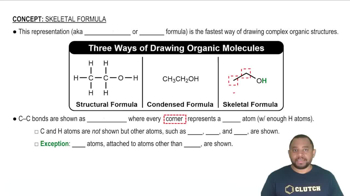
Chemical Formulas
A chemical formula represents the types and numbers of atoms in a molecule. For molecular compounds, the formula is typically written with the more electropositive element first, followed by the more electronegative element. For instance, in xenon tetrafluoride (XeF4), the formula indicates one xenon atom and four fluorine atoms, reflecting the molecular structure.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance