Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stereoisomerism
Stereoisomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula and connectivity of atoms but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms. This can lead to different physical and chemical properties. The two main types of stereoisomerism are geometric (cis-trans) and optical isomerism, which involves chiral centers.
Recommended video:
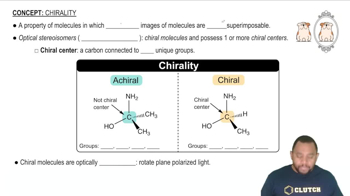
Chirality
Chirality is a property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image, much like left and right hands. A chiral molecule typically has one or more chiral centers, usually carbon atoms bonded to four different substituents. The presence of chirality in a compound can lead to the existence of enantiomers, which are pairs of stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other.
Recommended video:
Structural Representation
Structural representation involves depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, which is crucial for understanding its stereochemistry. Common methods include Lewis structures, condensed formulas, and skeletal structures. For compounds exhibiting stereoisomerism, it is important to accurately represent the 3D orientation of substituents to distinguish between different isomers.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance