Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms. In the case of C3H7NO, the different structures can arise from variations in the connectivity of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms, leading to distinct functional groups and properties. Understanding structural isomers is crucial for identifying and drawing the various forms of a compound.
Recommended video:
Functional Groups
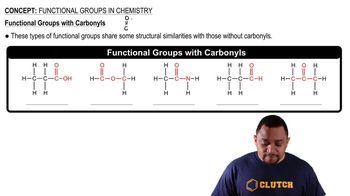
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the context of C3H7NO, the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) is significant, as it defines the reactivity and classification of the compound, such as whether it is an amide, ketone, or aldehyde. Identifying functional groups is essential for understanding the behavior of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Carbonyl Group
The carbonyl group is a functional group characterized by a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). It is a key feature in many organic compounds, influencing their reactivity and properties. In the context of C3H7NO, recognizing how the carbonyl group interacts with other atoms in the molecule helps in drawing the correct structures and predicting their chemical behavior.
Recommended video:
Carbonyl Functional Groups
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance