A 20.0-mL sample of 0.115 M sulfurous acid (H2SO3) solution is titrated with 0.1014 M KOH. At what added volume of base solution does each equivalence point occur?
Ch.17 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
Chapter 17, Problem 83
Referring to Table 17.1, pick an indicator for use in the titration
of each acid with a strong base.
a. HF
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Determine the pH range at the equivalence point for the titration of HF with a strong base. HF is a weak acid, and its titration with a strong base will result in a slightly basic equivalence point, typically around pH 8-9.
Refer to the provided color chart to identify indicators that change color in the pH range of 8-9.
From the chart, identify the indicators that have a color change range that includes pH 8-9. These indicators are Phenolphthalein and Thymolphthalein.
Select an indicator that has a clear and distinct color change within the pH range of 8-9. Phenolphthalein changes from colorless to pink in the pH range of approximately 8.2 to 10, making it a suitable choice.
Confirm that the chosen indicator (Phenolphthalein) will provide a clear endpoint for the titration of HF with a strong base by ensuring its color change range aligns with the expected pH at the equivalence point.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Titration
Acid-base titration is a quantitative analytical method used to determine the concentration of an acid or base in a solution. It involves the gradual addition of a titrant (strong base) to a solution of analyte (weak acid) until the reaction reaches the equivalence point, where the amount of acid equals the amount of base. The endpoint is often indicated by a color change, which is facilitated by an appropriate pH indicator.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Titration
pH Indicators
pH indicators are substances that change color in response to changes in pH, allowing for the visual determination of acidity or alkalinity in a solution. Each indicator has a specific pH range over which it changes color, making it suitable for different types of titrations. Selecting the right indicator is crucial for accurately identifying the endpoint of a titration, especially when titrating weak acids with strong bases.
Recommended video:
Guided course
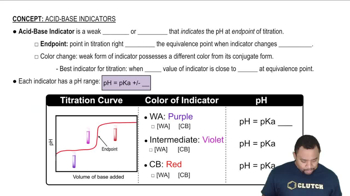
Acid-Base Indicators
Weak Acids vs. Strong Bases
Weak acids, like hydrofluoric acid (HF), do not completely dissociate in solution, resulting in a higher pH at the equivalence point compared to strong acids. When titrating a weak acid with a strong base, the pH at the equivalence point will be greater than 7, necessitating the use of a pH indicator that changes color in this range. Understanding the behavior of weak acids in titrations is essential for selecting the appropriate indicator from the provided table.
Recommended video:
Guided course
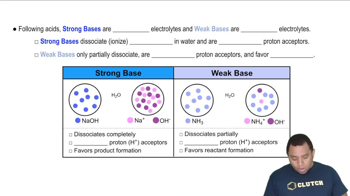
Strong vs Weak Bases
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1618
views
Textbook Question
Methyl red has a pKa of 5.0 and is red in its acid form and yellow in its basic form. If several drops of this indicator are placed in a 25.0-mL sample of 0.100 M HCl, what color will the solution appear? If 0.100 M NaOH is slowly added to the HCl sample, in what pH range will the indicator change color?
2078
views
1
rank
Open Question
Phenolphthalein has a pKa of 9.7. It is colorless in its acid form and pink in its basic form. For each of the following pH values, determine whether [In-] > [HIn] and predict the color of a phenolphthalein solution: a. pH = 2.0 b. pH = 5.0 c. pH = 8.0 d. pH = 11.0
Textbook Question
Referring to Table 17.1, pick an indicator for use in the titration of each base with a strong acid. a. CH3NH2
954
views
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations and expressions for Ksp for the dissolution of each ionic compound. a. BaSO4
927
views
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations and expressions for Ksp for the dissolution of each ionic compound. b. PbBr2
339
views
