Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Titration
Acid-base titration is a quantitative analytical method used to determine the concentration of an acid or base in a solution. In this process, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is gradually added to a solution of unknown concentration until the reaction reaches its equivalence point, indicated by a color change due to an indicator. This technique is fundamental in chemistry for analyzing the strength and concentration of acids and bases.
Recommended video:
Indicators
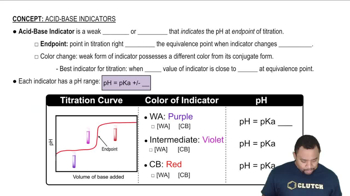
Indicators are substances that change color at a specific pH range, making them useful for determining the endpoint of a titration. Different indicators have different pH transition ranges, which means they are suitable for different types of titrations. For example, phenolphthalein changes from colorless to pink around pH 8.2 to 10, making it ideal for strong acid-weak base titrations, while methyl red changes from red to yellow between pH 4.4 and 6.2.
Recommended video:
pH Scale
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution, ranging from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic), with 7 being neutral. The pH of a solution affects the behavior of acids, bases, and indicators during titration. Understanding the pH scale is crucial for selecting the appropriate indicator for a titration, as the indicator must change color at a pH that corresponds to the expected equivalence point of the reaction.
Recommended video: