Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. a. 100.0 mL of 0.10 M NH3; 100.0 mL of 0.15 M NH4Cl
Ch.17 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
Chapter 17, Problem 53d
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. d. 175.0 mL of 0.10 M NH3; 150.0 mL of 0.12 M NaOH

Verified Solution
Video duration:
6mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buffer Solutions
A buffer solution is a system that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffers are crucial in maintaining stable pH levels in various chemical and biological processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Buffer Solutions
Weak Bases and Strong Bases
Weak bases, like ammonia (NH3), partially ionize in solution, establishing an equilibrium between the base and its conjugate acid (NH4+). In contrast, strong bases, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), fully dissociate in solution, leading to a significant increase in hydroxide ions (OH-). Understanding the behavior of these bases is essential for determining buffer capacity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
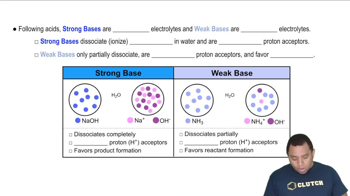
Strong vs Weak Bases
Concentration and Volume in Solution Chemistry
The concentration of a solution, expressed in molarity (M), indicates the amount of solute per liter of solution. When mixing solutions, the total volume and the concentrations of the individual components must be considered to determine the final concentrations of the resulting mixture. This is important for assessing whether the mixture can act as a buffer.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Constant-Volume Calorimetry
Related Practice
Textbook Question
637
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. b. 50.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl; 35.0 mL of 0.150 M NaOH
472
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. c. 50.0 mL of 0.15 M HF; 20.0 mL of 0.15 M NaOH
393
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. e. 125.0 mL of 0.15 M NH3; 150.0 mL of 0.20 M NaOH
526
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. c. 165.0 mL of 0.10 M HF; 135.0 mL of 0.050 M KOH
487
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. e. 105.0 mL of 0.15 M CH3NH2; 95.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl
738
views
