Textbook Question
Determine the [OH–], pH, and pOH of a 0.15 M ammonia solution.
1581
views
1
rank

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

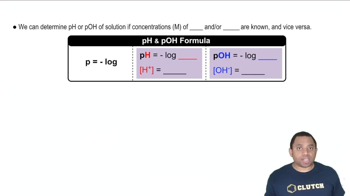

Determine the [OH–], pH, and pOH of a 0.15 M ammonia solution.
Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is a weak base with a pKb of 10.4. Calculate the pH of a solution containing a caffeine concentration of 455 mg/L.
Amphetamine (C9H13N) is a weak base with a pKb of 4.2. Calculate the pH of a solution containing an amphetamine concentration of 225 mg/L.
Determine if each anion acts as a weak base in solution. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. a. Br– b. ClO– c. CN– d. Cl–
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. a. C7H5O2– b. I– d. F–