Identify each substance as an acid or a base and write a chemical equation showing how it is an acid or a base according to the Arrhenius definition. a. HNO3(aq) b. NH4+(aq) d. HC2H3O2(aq)
Ch.16 - Acids and Bases
Chapter 16, Problem 126b,c
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base from among the reactants in each equation. b. AlBr3 + NH3 ⇌ H3NAlBr3 c. F–(aq) + BF3(aq) ⇌ BF4–(aq)

Verified Solution
Video duration:
55sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis acids are substances that can accept an electron pair, while Lewis bases are those that can donate an electron pair. This definition expands the concept of acids and bases beyond protons, focusing instead on electron pair interactions. Understanding this distinction is crucial for identifying the roles of reactants in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Acids and Bases
Electron Pair Donation
In the context of Lewis theory, electron pair donation refers to the process by which a Lewis base donates a pair of electrons to a Lewis acid. This interaction forms a coordinate covalent bond, where both electrons in the bond originate from the base. Recognizing which reactant donates the electron pair is essential for determining the Lewis base in a reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Coordination Complex Formation
Coordination complexes are formed when a Lewis acid and a Lewis base interact, resulting in a new compound where the acid accepts an electron pair from the base. This concept is fundamental in understanding many chemical reactions, particularly in transition metal chemistry, where such complexes play a significant role in reactivity and stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course
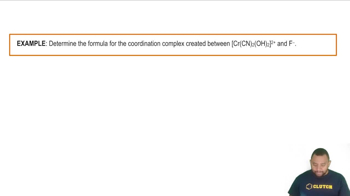
Coordination Complexes Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
884
views
Textbook Question
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. a. H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) c. HNO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
339
views
Textbook Question
Calculate [H3O+] and [OH–] for each solution at 25 °C. b. pH = 11.23 c. pH = 2.87
646
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. a. C7H5O2– b. I– d. F–
Textbook Question
Determine if each salt will form a solution that is acidic, basic, or pH-neutral. a. FeCl3 b. NaF c. CaBr2 d. NH4Br
