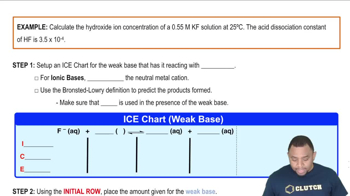
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis acids are defined as electron pair acceptors, while Lewis bases are electron pair donors. This theory expands the traditional definitions of acids and bases beyond protons, focusing instead on the transfer of electron pairs. Understanding this concept is crucial for classifying chemical species based on their ability to donate or accept electrons.
Recommended video:
Electron Pair Donation
A Lewis base donates an electron pair to form a covalent bond with a Lewis acid. This donation is a key characteristic of Lewis bases, which often contain lone pairs of electrons that can be shared. Recognizing the presence of these lone pairs in a species helps in identifying its role in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Hydroxide Ion (OH⁻)
The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) is a common example of a Lewis base due to its ability to donate a lone pair of electrons from the oxygen atom. This characteristic allows it to interact with Lewis acids, facilitating various chemical reactions. Understanding the properties of hydroxide is essential for classifying it correctly in the context of Lewis acid-base theory.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example