Textbook Question
Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). a. HNO3
469
views

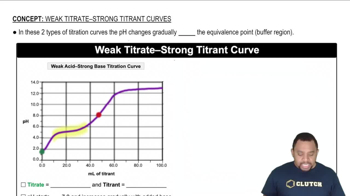


Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). a. HNO3
Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). b. HCl
Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). c. HBr
Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). a. HF
Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). b. HCHO2
Classify each acid as strong or weak. If the acid is weak, write an expression for the acid ionization constant (Ka). c. H2SO4