Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
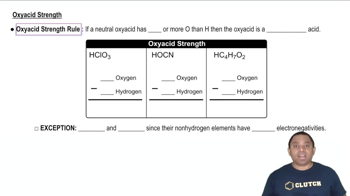
Oxyacid Strength
The strength of oxyacids is influenced by the number of oxygen atoms bonded to the central atom and the electronegativity of that central atom. Generally, more oxygen atoms increase the acid's strength due to greater resonance stabilization of the conjugate base. Additionally, higher electronegativity of the central atom leads to stronger acids as it stabilizes the negative charge on the conjugate base.
Recommended video:
Resonance Stabilization
Resonance stabilization occurs when a molecule can be represented by multiple valid Lewis structures, allowing for the delocalization of electrons. In oxyacids, the conjugate base can often be stabilized through resonance, which lowers the energy of the species and increases the acid's strength. The more resonance structures available, the more stable the conjugate base, leading to a stronger acid.
Recommended video:
Electronegativity Trends
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a bond. In the context of oxyacids, the central atom's electronegativity affects the acid's strength. For example, as you move from iodine (I) to bromine (Br) to chlorine (Cl) in the periodic table, the electronegativity increases, which typically results in stronger acids due to better stabilization of the conjugate base.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance