Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid Strength
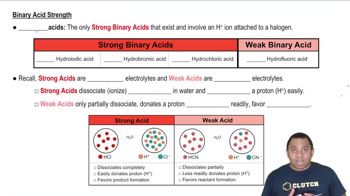
Acid strength refers to the ability of a compound to donate protons (H+) in a solution. Strong acids completely dissociate in water, while weak acids only partially dissociate. The strength of binary acids, which consist of hydrogen and one other element, often increases with the size and electronegativity of the non-hydrogen element.
Recommended video:
Binary Acids
Binary acids are compounds formed from hydrogen and one other nonmetal element. The general formula is HA, where A is a nonmetal. The strength of binary acids typically increases down a group in the periodic table due to the decreasing bond strength between hydrogen and the nonmetal, making it easier for the acid to release a proton.
Recommended video:
Electronegativity and Bond Strength
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a bond. In binary acids, higher electronegativity of the nonmetal can lead to stronger H-A bonds, but as you move down a group, larger atomic size results in weaker bonds. This interplay affects the acid's ability to dissociate and thus its strength, with larger, less electronegative atoms generally leading to stronger acids.
Recommended video: