Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
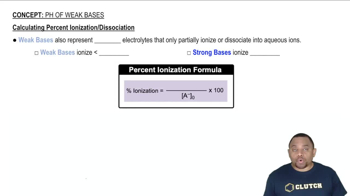
Weak Bases and Their Ionization
Weak bases, like quinine (Q), do not fully ionize in solution. Instead, they establish an equilibrium between the base and its conjugate acid when dissolved in water. The degree of ionization is characterized by the base dissociation constant (Kb), which quantifies the strength of the base in terms of its ability to accept protons.
Recommended video:
Calculating Percent Ionization of Weak Bases
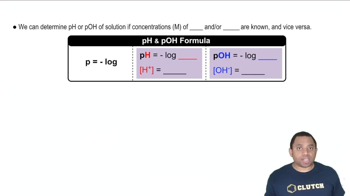
pH and pOH Relationship
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidity or basicity. The relationship between pH and pOH is given by the equation pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C. In this case, knowing the pH allows us to calculate the pOH, which is essential for determining the concentration of hydroxide ions in the solution, a key factor in calculating Kb.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Expressions and Kb Calculation
The Kb of a weak base is derived from its equilibrium expression, which relates the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium. For the dissociation of a weak base, Kb = [BH+][OH-] / [B], where [B] is the concentration of the base, [BH+] is the concentration of the conjugate acid, and [OH-] is the concentration of hydroxide ions. This relationship is crucial for calculating Kb from the given pH.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Constant Expressions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance