Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Partial Pressure
Partial pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a single component of a gas mixture. In the context of scuba diving, as a diver descends, the total pressure increases, which also raises the partial pressure of the gases they breathe, including oxygen. This relationship is described by Dalton's Law, which states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of its individual gases.
Recommended video:
Partial Pressure Calculation
Oxygen Toxicity
Oxygen toxicity occurs when the partial pressure of oxygen in the bloodstream becomes excessively high, leading to harmful physiological effects. Symptoms can include visual disturbances, seizures, and lung damage. This condition is particularly relevant for divers, as breathing oxygen at pressures above 1.4 atm can overwhelm the body's ability to process oxygen safely, resulting in toxicity.
Recommended video:
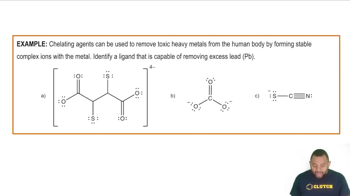
Classification of Ligands Example
Reversal of Oxygen Toxicity
Reversing oxygen toxicity primarily involves reducing the partial pressure of oxygen in the diver's environment. This can be achieved by ascending to shallower depths where the pressure is lower, thereby decreasing the partial pressure of oxygen in the lungs and bloodstream. Additionally, administering pure oxygen in a controlled environment can help manage symptoms and facilitate recovery.
Recommended video:
Reversible Changes in Matter
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance