Nitrogen has a normal boiling point of 77.3 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 63.1 K. Its critical temperature is 126.2 K and its critical pressure is 2.55×104 torr. It has a triple point at 63.1 K and 94.0 torr. Sketch the phase diagram for nitrogen. Does nitrogen have a stable liquid state at 1 atm?
Ch.11 - Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces
Chapter 11, Problem 77b
The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. b. Which of the two solid states of sulfur is more dense?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1> Identify the two solid states of sulfur mentioned in the problem: rhombic and monoclinic.
insert step 2> Understand that density is defined as mass per unit volume (density = mass/volume).
insert step 3> Recognize that in a phase diagram, the denser phase is typically the one that is stable at higher pressures for a given temperature.
insert step 4> Examine the phase diagram to determine which solid state (rhombic or monoclinic) is stable at higher pressures.
insert step 5> Conclude that the solid state stable at higher pressures is the more dense form of sulfur.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phase Diagram
A phase diagram is a graphical representation that shows the phases of a substance at various temperatures and pressures. It illustrates the boundaries between different states of matter, such as solid, liquid, and gas. Understanding phase diagrams is crucial for predicting the conditions under which a substance will exist in a particular phase, which is essential for answering questions about density in different states.
Recommended video:
Guided course
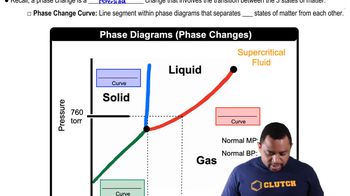
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is a key physical property of materials. It is typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). In the context of solid states of sulfur, comparing the densities of rhombic and monoclinic forms helps determine which structure is more compact and thus denser, influencing their physical properties and applications.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Density Concepts
Solid State Structures
Solid state structures refer to the arrangement of atoms or molecules in a solid material, which can significantly affect its properties, including density. Rhombic and monoclinic sulfur have different crystalline structures, leading to variations in how closely packed the sulfur atoms are. Understanding these structural differences is essential for determining which solid state is denser and why.
Recommended video:
Guided course
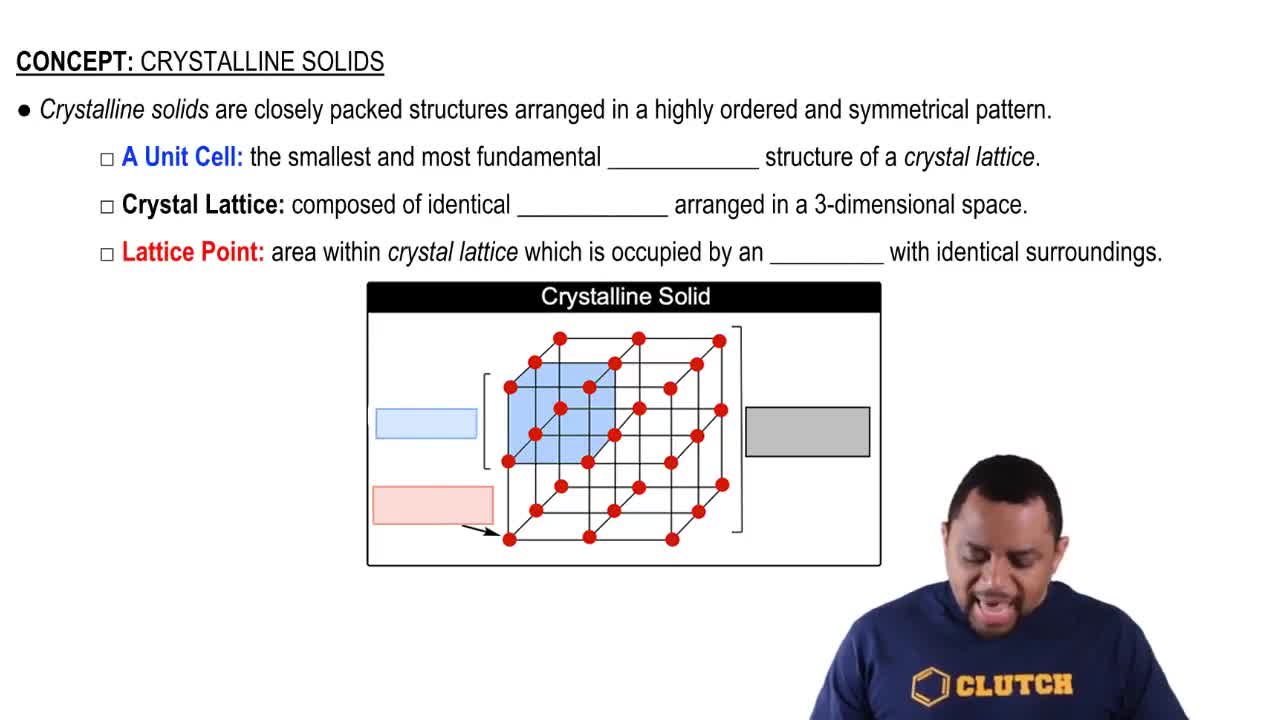
Crystalline Solids Structure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2550
views
Textbook Question
Argon has a normal boiling point of 87.2 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 84.1 K. Its critical temperature is 150.8 K and its critical pressure is 48.3 atm. It has a triple point at 83.7 K and 0.68 atm. Sketch the phase diagram for argon. Which has the greater density, solid argon or liquid argon?
2352
views
Textbook Question
The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. a. Below what pressure does solid sulfur sublime?
1585
views
Open Question
Water has a high boiling point given its relatively low molar mass. Why?
Textbook Question
Water is a good solvent for many substances. What is the molecular basis for this property, and why is it significant?
649
views
Open Question
Explain the role of water in moderating Earth's climate.
