For each molecular geometry, list the number of total electron groups, the number of bonding groups, and the number of lone pairs on the central atom. (c)
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
All textbooks Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 37
Problem 37
 Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 37
Problem 37Chapter 10, Problem 37
Which species has the smaller bond angle, H3O+ or H2O? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the molecular geometry of each species: H2O is bent, and H3O+ is trigonal pyramidal.
Consider the number of lone pairs on the central atom: H2O has two lone pairs, while H3O+ has one lone pair.
Recall that lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs, affecting bond angles.
Understand that more lone pairs result in smaller bond angles due to increased repulsion.
Conclude that H2O, with more lone pairs, has a smaller bond angle compared to H3O+.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, which influence the shape and angles between bonds. Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for predicting bond angles and the overall structure of molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs. According to VSEPR, electron pairs will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, which directly affects bond angles. This theory helps explain why H3O+ has a different bond angle compared to H2O.
Recommended video:
Guided course
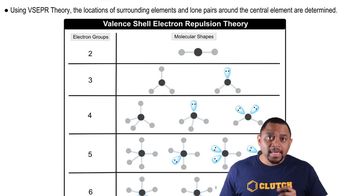
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
Bond Angles
Bond angles are the angles formed between two adjacent bonds at an atom. They are influenced by the number of lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons surrounding the atom. In the case of H3O+ and H2O, the presence of an additional hydrogen ion in H3O+ alters the bond angle compared to H2O, leading to a smaller angle due to increased electron repulsion.
Recommended video:
Guided course
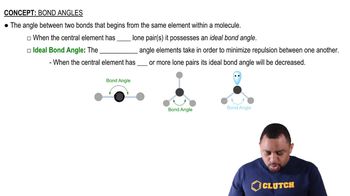
Bond Angles
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1241
views
Textbook Question
Determine the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and idealized bond angles for each molecule. In which cases do you expect deviations from the idealized bond angle? a. PF3 b. SBr2 c. CHCl3 d. CS2
1624
views
1
comments
Textbook Question
Determine the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and idealized bond angles for each molecule. In which cases do you expect deviations from the idealized bond angle? a. CF4 b. NF3 c. OF2 d. H2S
1172
views
Textbook Question
Which species has the smaller bond angle, ClO4- or ClO3- ? Explain.
998
views
Open Question
Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion using the bond conventions shown in “Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper” in Section 10.4 for the following: a. SF4 b. ClF3.
Textbook Question
Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion using the bond conventions shown in 'Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper' in Section 10.4. c. IF2-
468
views