Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion using the bond conventions shown in 'Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper' in Section 10.4. c. IF2-
 Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 40c
Problem 40cDetermine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion, using the bond conventions shown in 'Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper' in Section 10.4. c. PF5
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
VSEPR Theory
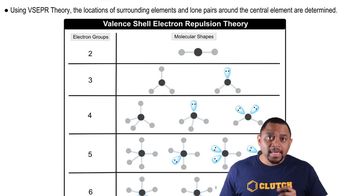
Molecular Geometry

Phosphorus Pentafluoride (PF5)

Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion using the bond conventions shown in 'Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper' in Section 10.4. d. IBr4-
Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion, using the bond conventions shown in 'Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper' in Section 10.4. b. SCl6
Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion, using the bond conventions shown in 'Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper' in Section 10.4. d. IF4+
Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and draw each molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.)
a. C2H2 (skeletal structure HCCH)
b. C2H4 (skeletal structure H2CCH2)
c. C2H6 (skeletal structure H3CCH3)
Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. a. N2