Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each molecule or ion. Sketch the structure, including overlapping orbitals, and label all bonds using the notation shown in Examples 10.6 and 10.7. a. SO32-
 Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 67
Problem 67Consider the structure of the amino acid alanine. Indicate the hybridization about each interior atom.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Hybridization

Amino Acids Structure
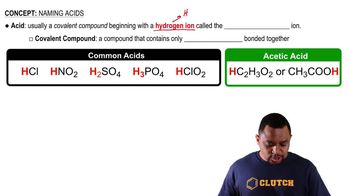
Bond Angles and Molecular Geometry
Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each molecule that contains more than one interior atom. Indicate the hybridization about each interior atom. Sketch the structure, including overlapping orbitals, and label all bonds using the notation shown in Examples 10.6 and 10.7. a. N2H2 (skeletal structure HNNH) b. N2H4 (skeletal structure H2NNH2) c. CH3NH2 (skeletal structure H3CNH2)
Write a hybridization and bonding scheme for each molecule that contains more than one interior atom. Indicate the hybridization about each interior atom. Sketch the structure, including overlapping orbitals, and label all bonds using the notation shown in Examples 10.6 and 10.7. c. C2H6 (skeletal structure H3CCH3)
Consider the structure of the amino acid aspartic acid. Indicate the hybridization about each interior atom.
Sketch the bonding molecular orbital that results from the linear combination of two 1s orbitals. Indicate the region where interference occurs and state the kind of interference (constructive or destructive).
Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2- . Do you expect these molecules to exist in the gas phase?