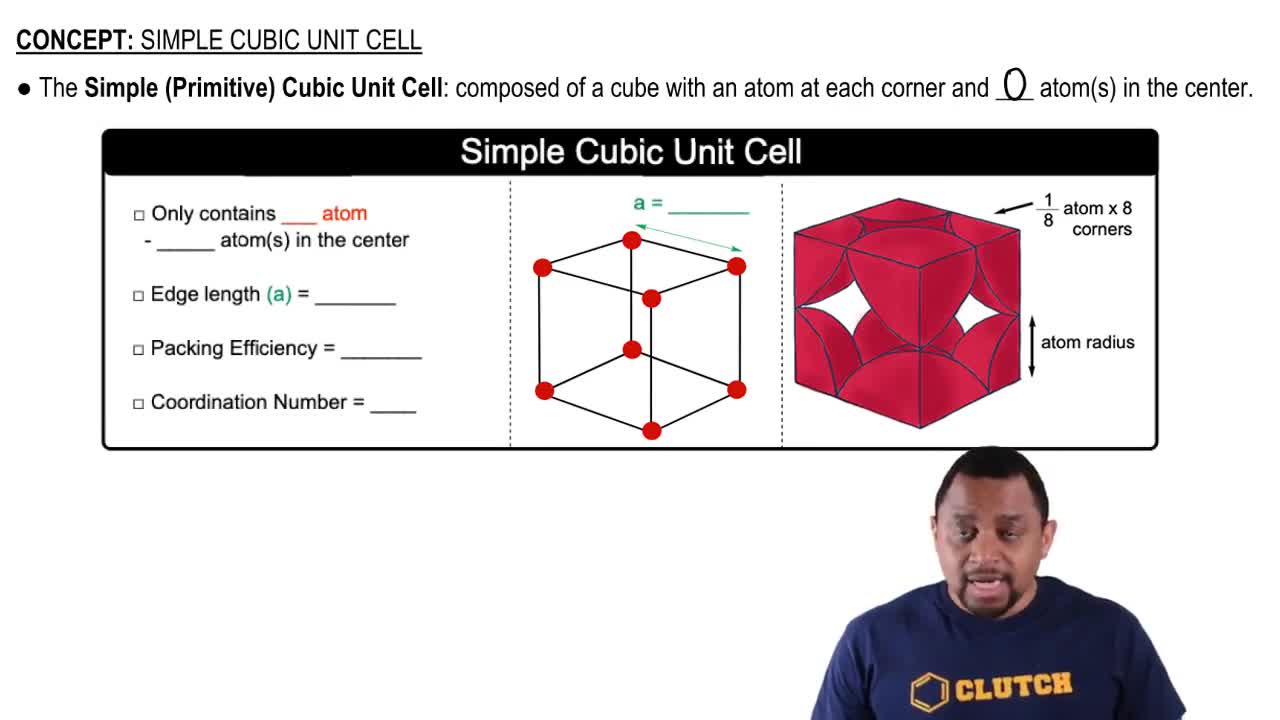
Open Question
What is the packing efficiency of a face-centered cubic unit cell? Please show your work.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Platinum crystallizes with the face-centered cubic unit cell. The radius of a platinum atom is 139 pm. Calculate the edge length of the unit cell and the density of platinum in g/cm3.
Molybdenum crystallizes with the body-centered unit cell. The radius of a molybdenum atom is 136 pm. Calculate the edge length of the unit cell and the density of molybdenum
Barium has a density of 3.59 g/cm3 and crystallizes with the body-centered cubic unit cell. Calculate the radius of a barium atom.
Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. a. Ar(s) b. H2O(s) c. K2O(s) d. Fe(s)