Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
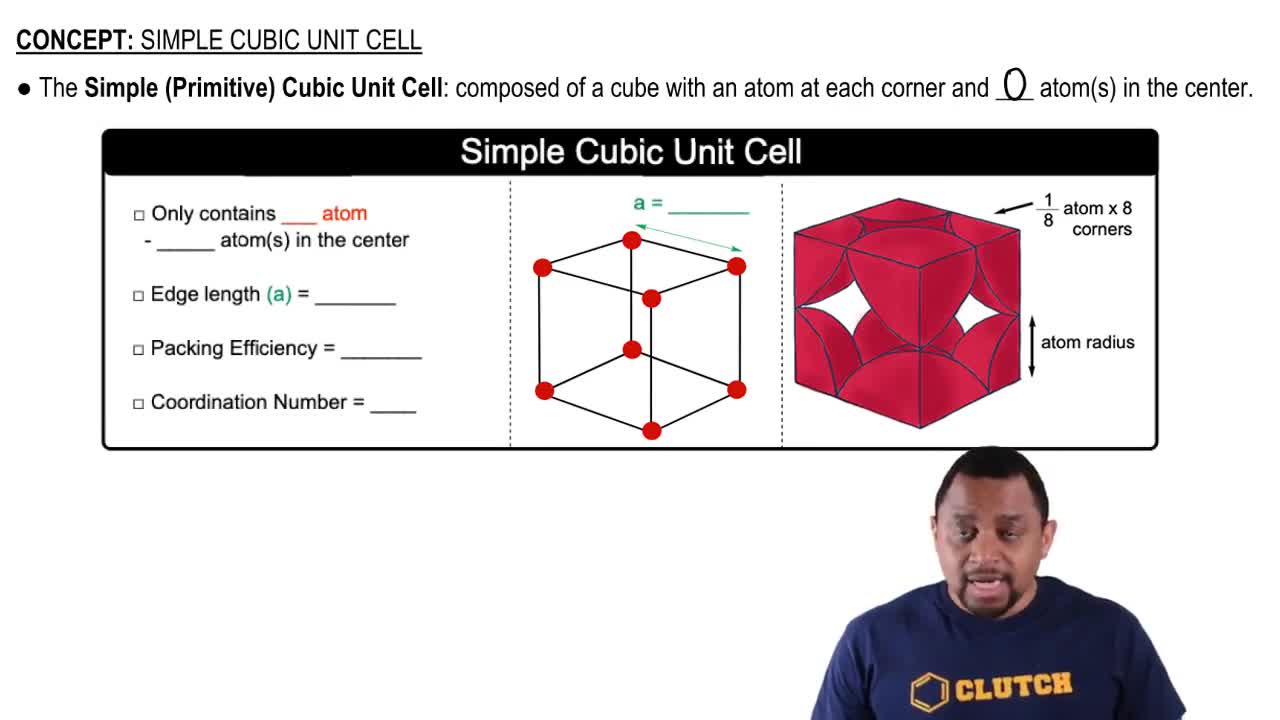
Unit Cell
A unit cell is the smallest repeating unit in a crystal lattice that reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal. It defines the arrangement of atoms in a solid and is characterized by its dimensions and angles. Understanding the unit cell is crucial for determining the number of atoms it contains, which can vary based on the type of crystal structure (e.g., face-centered cubic, body-centered cubic).
Recommended video:
Atomic Packing Factor (APF)
The Atomic Packing Factor (APF) is a measure of how efficiently atoms are packed in a unit cell. It is calculated as the volume occupied by the atoms in the unit cell divided by the total volume of the unit cell. Different metals have different APFs depending on their crystal structures, which influences their physical properties and density.
Recommended video:
Coordination Number
The coordination number is the number of nearest neighbor atoms surrounding a central atom in a crystal structure. It provides insight into the arrangement of atoms and the bonding characteristics within the metal. For example, tungsten has a body-centered cubic structure with a coordination number of 8, indicating that each tungsten atom is surrounded by eight other tungsten atoms.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance