Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
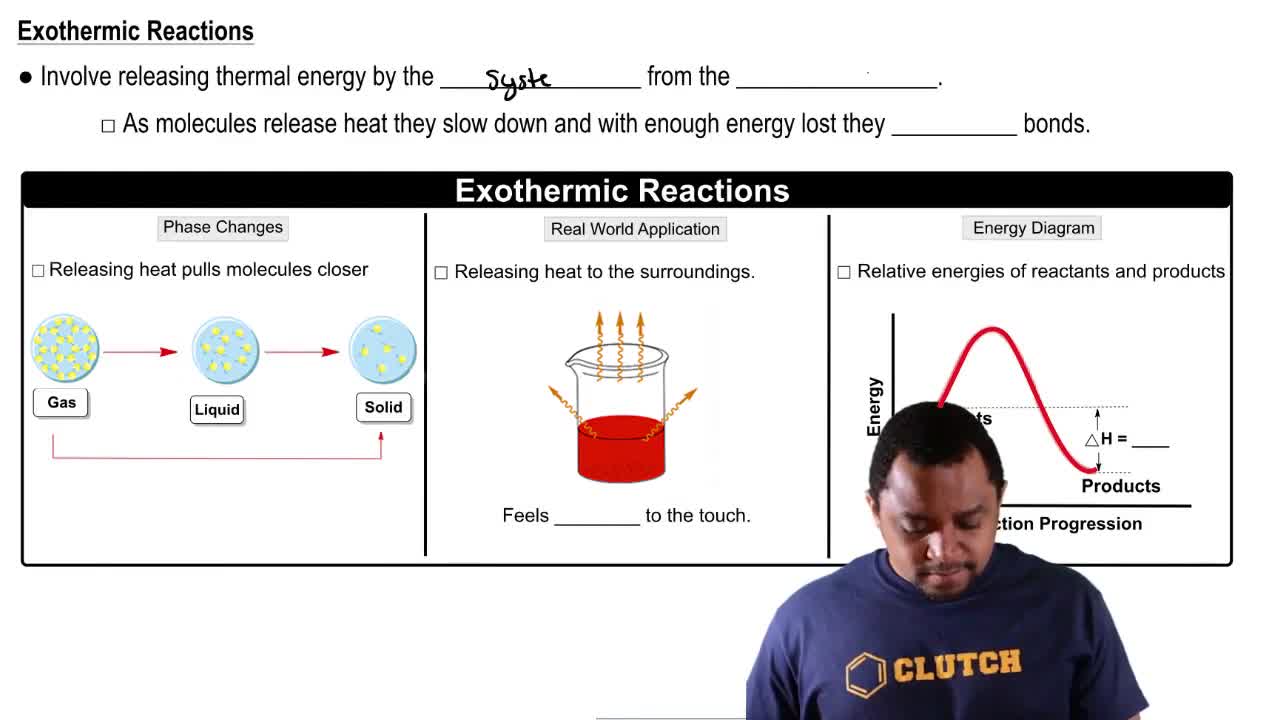
Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are chemical processes that release energy in the form of heat. In the context of the hot pack, the dissolution of LiCl in water is an exothermic reaction, which means that as the solid dissolves, it releases heat, causing the temperature of the solution to rise. This concept is crucial for understanding how the hot pack generates heat and increases in temperature.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius. For the solution in the hot pack, the specific heat capacity is given as 4.18 J/g°C. This property is essential for calculating the temperature change of the solution when heat is added due to the dissolution of LiCl, allowing us to determine the final temperature of the hot pack.
Recommended video:
Heat Transfer Calculations
Heat transfer calculations involve determining the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction or physical process. In this scenario, we can use the formula q = mcΔT, where q is the heat absorbed, m is the mass of the solution, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature. This calculation is vital for finding the final temperature of the hot pack after the dissolution of LiCl.
Recommended video:
Calculations with Heating and Cooling Curves