Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electron-Dot Structures
Electron-dot structures, or Lewis structures, represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. They illustrate how atoms are bonded together and show lone pairs of electrons. In the context of amino acids like histidine, these structures help visualize the connectivity and bonding, including single, double, or triple bonds, which are crucial for understanding molecular geometry and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Hybridization
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can accommodate bonding. The type of hybridization (sp, sp2, sp3) depends on the number of bonds and lone pairs around a central atom. For example, sp hybridization indicates a linear arrangement with two regions of electron density, while sp3 indicates a tetrahedral arrangement with four regions, which is essential for determining the geometry of molecules like histidine.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Structure
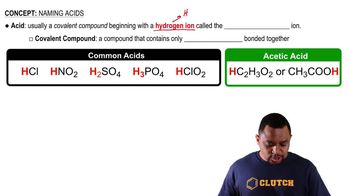
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable R group. The specific structure of amino acids, including functional groups and their connectivity, influences their chemical properties and interactions, which is critical for understanding biochemical processes and protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Acids and Their Structure
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 7
Problem 7