Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are a set of numerical values that describe the unique quantum state of an electron in an atom. There are four quantum numbers: the principal quantum number (n), the azimuthal quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml), and the spin quantum number (ms). Each quantum number has specific rules governing its possible values, which are essential for determining the allowed states of electrons.
Recommended video:
Principal Quantum Number (n) and Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
The principal quantum number (n) indicates the energy level of an electron and can take positive integer values (1, 2, 3, ...). The azimuthal quantum number (l) defines the shape of the orbital and can take values from 0 to (n-1). Therefore, for a given n, l must always be less than n, which is crucial for determining the validity of the quantum number combinations.
Recommended video:
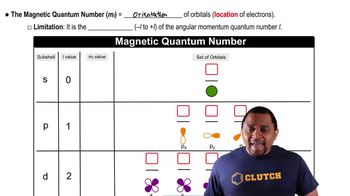
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
The magnetic quantum number (ml) specifies the orientation of the orbital in space and can take integer values ranging from -l to +l, including zero. This means that for each value of l, there are (2l + 1) possible values for ml. Understanding these restrictions is vital for identifying which combinations of quantum numbers are permissible.
Recommended video: