Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Orbitals (MOs)
Molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals when atoms bond together. In the case of cyclooctatetraene dianion, the p orbitals combine to form bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The arrangement and occupancy of these MOs determine the electronic properties of the molecule, including its magnetic behavior.
Recommended video:
Paramagnetism vs. Diamagnetism
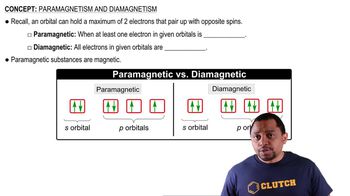
Paramagnetism occurs in species that have unpaired electrons, leading to a net magnetic moment that can align with an external magnetic field. In contrast, diamagnetism is exhibited by species with all electrons paired, resulting in no net magnetic moment. The presence of unpaired electrons in the molecular orbitals of cyclooctatetraene dianion will dictate whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Recommended video:
Paramagnetism vs Diamagnetism
Electron Configuration in MOs
The electron configuration in molecular orbitals is crucial for determining the magnetic properties of a molecule. Electrons fill the molecular orbitals starting from the lowest energy level, following the Pauli exclusion principle and Hund's rule. By analyzing the filling of the p molecular orbitals in cyclooctatetraene dianion, one can ascertain whether there are unpaired electrons, which would indicate paramagnetism.
Recommended video:
Electron Configuration Example