Textbook Question
How many milliliters of 1.00 M KOH must be added to neutralize the following solutions? (a) A mixture of 0.240 M LiOH (25.0 mL) and 0.200 M HBr (75.0 mL)
652
views


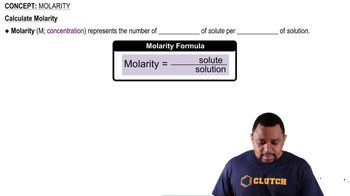

How many milliliters of 1.00 M KOH must be added to neutralize the following solutions? (a) A mixture of 0.240 M LiOH (25.0 mL) and 0.200 M HBr (75.0 mL)
How many milliliters of 1.00 M KOH must be added to neutralize the following solutions? (b) A mixture of 0.300 M HCl (45.0 mL) and 0.250 M NaOH (10.0 mL)
How many milliliters of 2.00 M HCl must be added to neutralize the following solutions? (a) A mixture of 0.160 M HNO3 (100.0 mL) and 0.100 M KOH (400.0 mL)
Assign oxidation numbers to each element in the following compounds. (a) NO2
Assign oxidation numbers to each element in the following compounds. (b) SO3