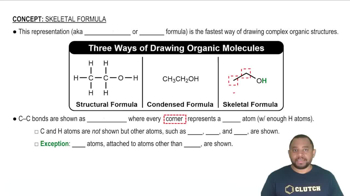
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Weight
Molecular weight, or molar mass, is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It is calculated by summing the atomic weights of all atoms in a molecular formula. Understanding how to determine molecular weight is essential for stoichiometric calculations in chemistry, as it allows for the conversion between grams of a substance and moles.
Recommended video:
Weight Conversion Example
Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized by increasing atomic number and grouped by similar properties. Each element's atomic weight is listed, which is crucial for calculating molecular weights. Familiarity with the periodic table enables students to quickly find the necessary atomic weights for elements in a compound.
Recommended video:
Periodic Table Classifications
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula represents the composition of a substance, indicating the types and numbers of atoms present. For example, Hg2Cl2 indicates that the compound contains two mercury (Hg) atoms and two chlorine (Cl) atoms. Understanding how to interpret chemical formulas is vital for determining the molecular weight and for grasping the relationships between different substances in chemical reactions.
Recommended video: