Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction with equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. This ensures the law of conservation of mass is upheld, meaning that matter is neither created nor destroyed during the reaction. Balancing involves adjusting coefficients in front of the chemical formulas to achieve this equality.
Recommended video:
Balancing Chemical Equations
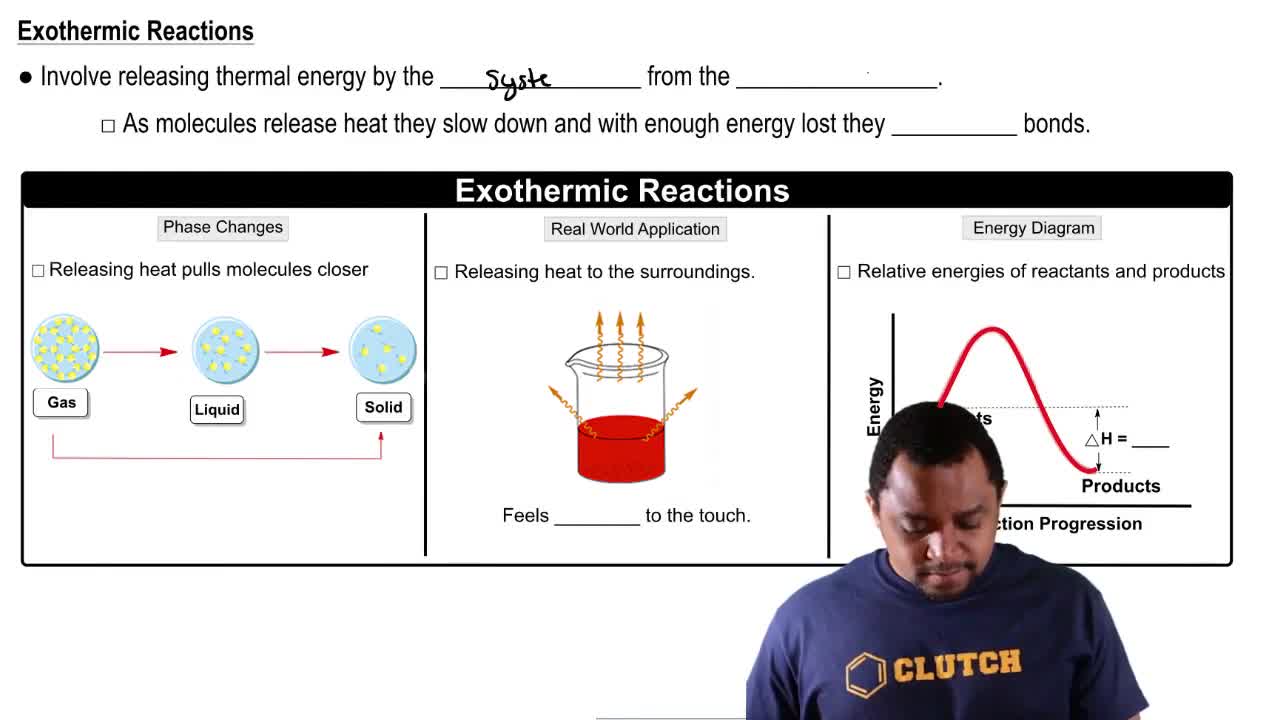
Exothermic Reaction
An exothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction that releases energy, usually in the form of heat, to its surroundings. This occurs when the total energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants, resulting in a net release of energy. Understanding this concept is crucial for predicting temperature changes and the direction of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
States of Matter
The states of matter refer to the distinct forms that different phases of matter take on, primarily solid, liquid, and gas. In the context of chemical reactions, the state of each reactant and product can influence reaction rates and equilibrium. Recognizing the states of matter involved helps in writing accurate chemical equations and understanding the behavior of substances during reactions.
Recommended video: