Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Le Châtelier's Principle
Le Châtelier's Principle states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the position of equilibrium shifts to counteract the change. This means that if a system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure, the equilibrium will shift in a direction that minimizes the effect of that change.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Constant (Kc)
The equilibrium constant (Kc) is a numerical value that expresses the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium for a given reaction at a specific temperature. Changes in temperature can affect the value of Kc; for exothermic reactions, increasing temperature typically decreases Kc, while decreasing temperature increases Kc, reflecting the shift in equilibrium position.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Constant Expressions
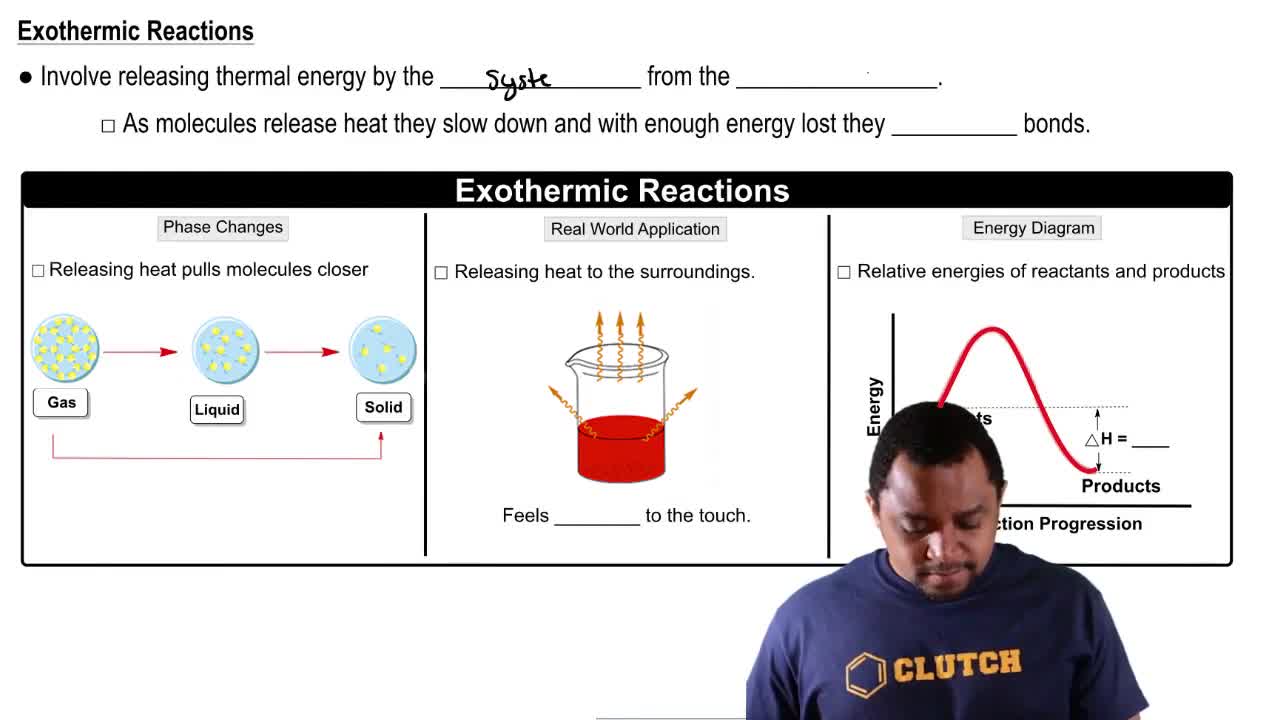
Exothermic Reactions
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases heat, resulting in a negative change in enthalpy (ΔH). In the context of the water-gas shift reaction, the release of heat means that increasing the temperature will favor the reactants, leading to a decrease in the amount of H2 in the equilibrium mixture, while decreasing the temperature will favor the formation of products, increasing Kc.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions