Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Le Chatelier's Principle
Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the position of equilibrium shifts to counteract the change. In the context of the given reaction, diluting the solution with water alters the concentration of the reactants and products, prompting the system to adjust in a way that minimizes the effect of dilution.
Recommended video:
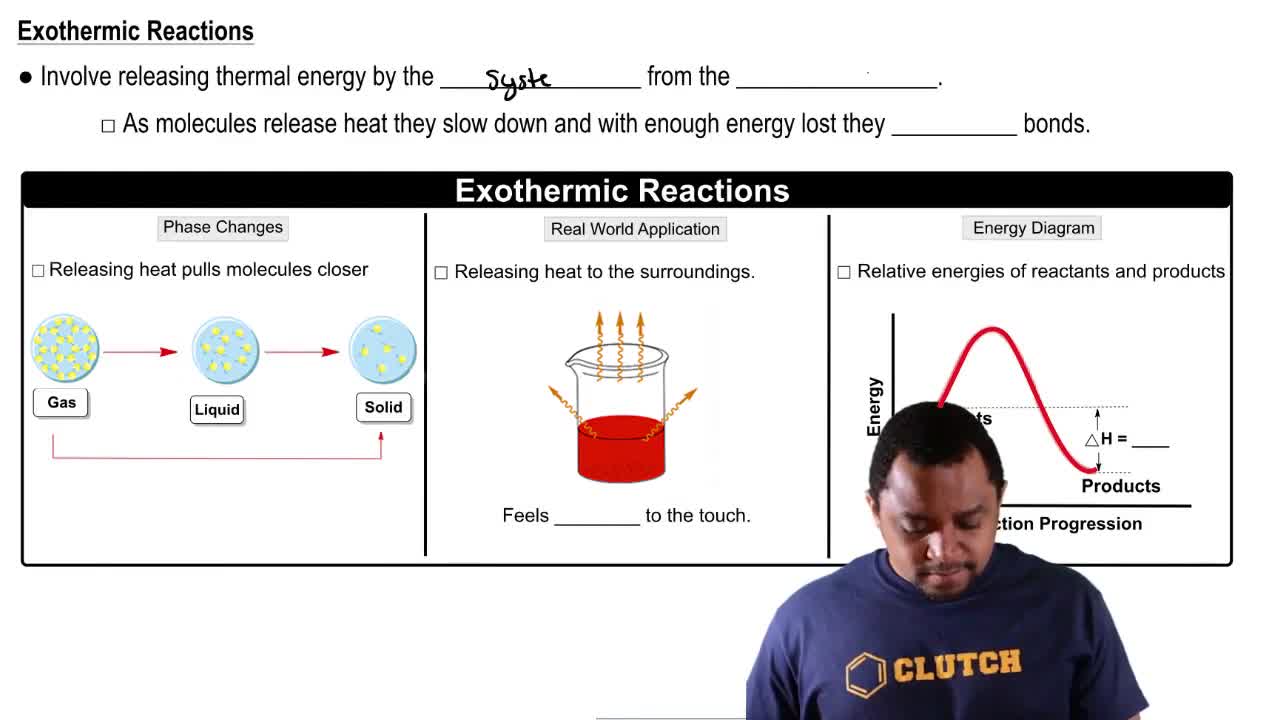
Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are chemical processes that release heat to the surroundings. In the provided reaction, the formation of Co(H2O)6^2+ and Cl^- ions from CoCl2 and water is exothermic, meaning that the reaction releases energy. Understanding this helps predict how temperature changes can affect the equilibrium position.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Color Change in Coordination Complexes
The color change observed in coordination complexes, such as the transition from blue CoCl2^- to pink Co(H2O)6^2+, is due to the different ligands surrounding the metal ion. The nature of the ligands and their arrangement affects the d-orbital splitting, which in turn influences the absorption of light and the perceived color. This concept is crucial for interpreting the effects of dilution on the equilibrium state.
Recommended video:
Coordination Complexes Example