Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
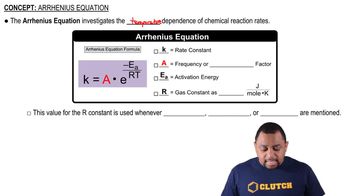
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant of a reaction to the temperature and activation energy. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation helps predict how changes in temperature affect reaction rates.
Recommended video:
Activation Energy (Ea)
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to form products. In the context of the Arrhenius equation, a lower Ea results in a higher rate constant, indicating that the reaction can proceed more quickly at a given temperature.
Recommended video:
Rate Constant (k)
The rate constant is a proportionality factor in the rate law of a chemical reaction, indicating the speed of the reaction. It varies with temperature and is influenced by factors such as activation energy and molecular collisions. For bimolecular reactions, the rate constant can be calculated using the Arrhenius equation, which incorporates temperature and activation energy.
Recommended video: