Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
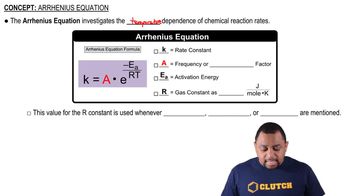
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation describes the temperature dependence of reaction rates. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. Understanding this equation is crucial for determining how temperature affects the rate of the thermal decomposition of nitrous oxide.
Recommended video:
Partial Pressure
Partial pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a single component of a gas mixture. According to Dalton's Law, the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of its individual components. In this question, knowing how to calculate and manipulate partial pressures is essential for determining the conditions under which the desired amount of O2 is produced in the exit gas.
Recommended video:
Partial Pressure Calculation
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases under various conditions of temperature, pressure, and volume. Key laws include Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, and the Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT). These principles are necessary for understanding how the flow rate, volume, and pressure of gases interact in the tube, which is critical for solving the problem regarding the thermal decomposition of nitrous oxide.
Recommended video: