Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
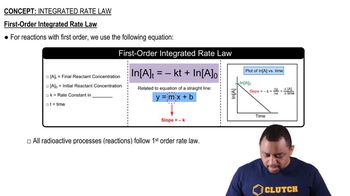
First-Order Reactions
First-order reactions are chemical reactions where the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant. In this case, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide follows first-order kinetics, meaning that as the concentration of H2O2 decreases, the rate of reaction also decreases. The half-life of a first-order reaction is constant, allowing for straightforward calculations of concentration over time.
Recommended video:
Gas Laws and PV Work
The ideal gas law relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas, and is crucial for calculating work done by gases. In this scenario, the work done (PV work) is calculated using the formula W = PΔV, where P is the external pressure and ΔV is the change in volume due to gas production. Understanding how to apply this law is essential for determining the energy changes in the system.
Recommended video:
Density and Volume Calculations
Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is critical for converting between mass and volume in solutions. Given that the density of the hydrogen peroxide solution is 1.00 g/mL, this allows for the calculation of the mass of H2O2 present in the reaction vessel. Accurate volume calculations are necessary to determine how much gas is produced and how it affects the piston movement.
Recommended video: