Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
van't Hoff Factor (i)
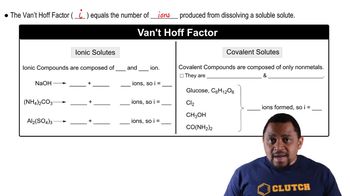
The van't Hoff factor (i) represents the number of particles into which a solute dissociates in solution. For ionic compounds like CaCl2, which dissociates into three ions (one Ca²⁺ and two Cl⁻), the theoretical van't Hoff factor is 3. However, the given value of 2.71 suggests some degree of ion pairing or incomplete dissociation in the solution.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression
Freezing point depression is a colligative property that describes how the freezing point of a solvent decreases when a solute is added. The relationship is given by the formula ΔTf = i * Kf * m, where ΔTf is the change in freezing point, Kf is the freezing point depression constant of the solvent, and m is the molality of the solution. This concept is essential for calculating the concentration of the solute based on the observed freezing point.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression
Mass Percent Concentration
Mass percent concentration is a way to express the concentration of a solute in a solution, defined as the mass of the solute divided by the total mass of the solution, multiplied by 100. It is crucial for determining how much of the solute is present in a given mass of solution, which can be derived from the molality and the density of the solution when solving problems related to colligative properties.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance