Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling point elevation is a colligative property that describes how the boiling point of a solvent increases when a solute is dissolved in it. This phenomenon occurs because the presence of solute particles disrupts the solvent's ability to evaporate, requiring a higher temperature to reach the boiling point. The relationship is quantified by the formula ΔT = Kb * m, where ΔT is the boiling point elevation, Kb is the boiling point elevation constant, and m is the molality of the solution.
Recommended video:
Molality
Molality (m) is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. It is particularly useful in colligative property calculations because it directly relates to the number of solute particles in a given mass of solvent, making it independent of temperature and volume changes. The formula for calculating molality is m = moles of solute / mass of solvent (in kg).
Recommended video:
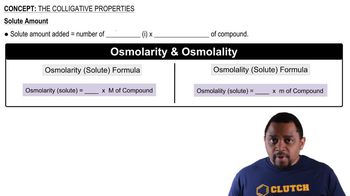
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, vapor pressure lowering, and osmotic pressure. Understanding colligative properties is essential for predicting how the addition of solute affects the physical properties of a solvent, which is crucial in various chemical applications.
Recommended video: