Ocean currents are measured in Sverdrups (sv) where 1 sv = 109 m3/s. The Gulf Stream off the tip of Florida, for instance, has a flow of 35 sv. (b) What mass of water in the Gulf Stream flows past a given point in 24 hours? The density of seawater is 1.025 g/mL.
The element gallium (Ga) has the second-largest liquid range of any element, melting at 29.78 °C and boiling at 2204 °C at atmospheric pressure. (b) Assume that you construct a thermometer using gallium as the fluid instead of mercury and that you define the melting point of gallium as 0 °G and the boiling point of gallium as 1000 °G. What is the melting point of sodium chloride (801 °C) on the gallium scale?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
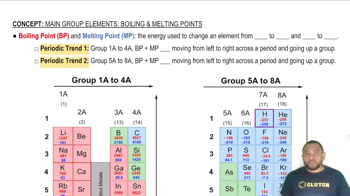
Melting and Boiling Points
Temperature Scales

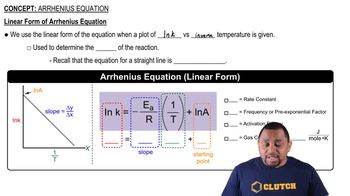
Linear Interpolation
Ocean currents are measured in Sverdrups (sv) where 1 sv = 109 m3/s. The Gulf Stream off the tip of Florida, for instance, has a flow of 35 sv. (c) How much time is required for 1 petaliter (PL; 1 PL = 1015 L) of seawater to flow past a given point?
The element gallium (Ga) has the second-largest liquid range of any element, melting at 29.78 °C and boiling at 2204 °C at atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the density of gallium in g/cm3 at 25 °C if a 1 in. cube has a mass of 0.2133 lb?
The Rankine temperature scale used in engineering is to the Fahrenheit scale as the Kelvin scale is to the Celsius scale. That is, 1 Rankine degree is the same size as 1 Fahrenheit degree, and 0 °R = absolute zero. (a) What temperature corresponds to the freezing point of water on the Rankine scale?
